Credit is a financial service that allows individuals or businesses to borrow money with the promise to repay it over time with interest.
The ability to obtain and use credit responsibly can be a valuable tool for meeting long-term financial goals.
However, in order to have access to loans or credit cards, financial institutions evaluate the applicant's creditworthiness.
What is credit?
Credit refers to the ability to obtain money or goods now, with the promise to repay them in the future.
It is a financial tool that allows individuals and businesses to access resources that they would not otherwise be able to obtain.
Credit can be used to finance major purchases, such as a house or car, or to cover unexpected expenses such as a medical emergency.
To extend credit, financial institutions evaluate the risk of lending money to a person or business.
This is where credit history and credit scores come into play. Lenders use this information to determine whether to extend credit and at what interest rate.
Types of Credit
There are several types of credit you can obtain, each with its own characteristics and requirements:
- Consumer credit: used to finance personal or family expenses, such as the purchase of an appliance or a vacation;
- Mortgage loan: used to buy a house or land. It usually has a long term (up to 30 years) and a lower interest rate than consumer credit;
- Auto loan: used to buy a new or used vehicle. It usually has a medium term (up to 5 years) and an interest rate similar to the mortgage loan;
- Credit card: allows you to make purchases on credit at commercial establishments or online.
Personal loans
Personal loans are loans granted to an individual without the need for specific collateral.
Mortgage loans
Mortgage loans are those that are granted with the guarantee of a real estate property, generally a house.
This type of loan usually has longer terms and lower interest rates than other types of loans.
Automobile loans
Auto loans are loans granted for the purchase of a vehicle, whether new or used.
Business loans
Business loans are loans intended to finance a business or a venture.
These loans may be granted by banking institutions, financial cooperatives or even by the government.
Student loans
Student loans are loans granted to students to finance their studies.
These loans can be granted by both private and governmental entities and usually have lower interest rates and more flexible repayment terms than other types of loans.
How Credit Scores Work
Credit scores, also known as credit scores, are a system used by lenders and banks to assess the risk of granting a loan or credit to a customer.
The credit score is calculated from information found in the customer's credit history, such as payment history, account balance, length of time the customer has had credit and amount of credit available.
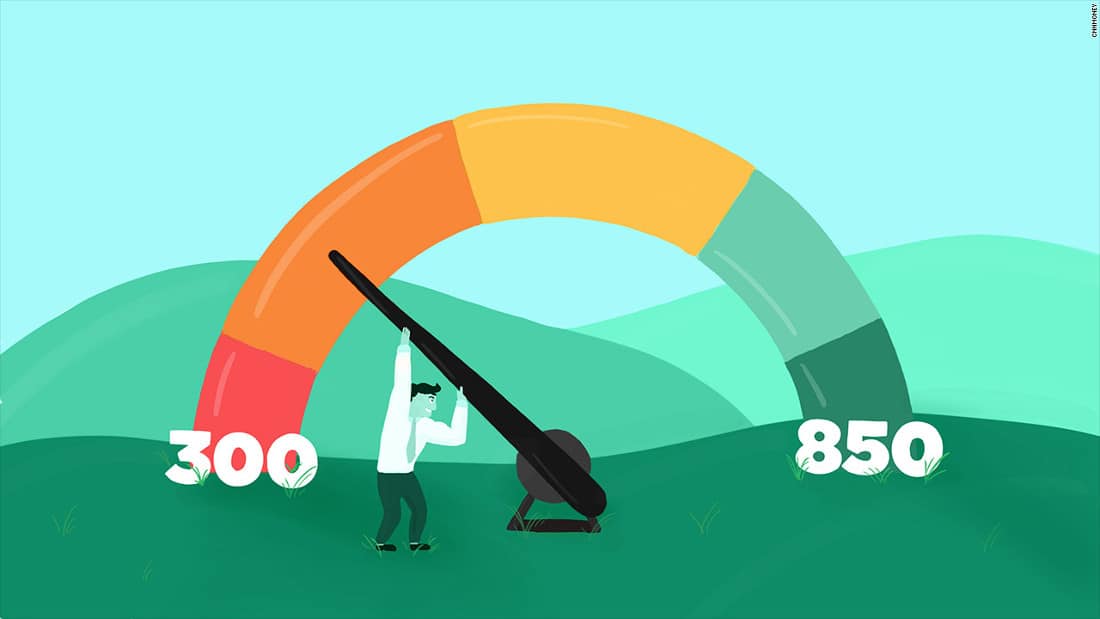
The score can range from 300 to 850 points, with 300 being the lowest and 850 the highest. A higher score indicates greater creditworthiness and less risk to lenders.
It is important to note that each credit rating agency (such as Equifax, Experian or TransUnion) may use different formulas to calculate credit scores.
What are credit scores
A credit score is a number that represents the likelihood that a person will pay his or her debts on time.
This number is based on information from credit reports and is used to determine whether a person is eligible for a loan, credit card or mortgage.
The credit score is calculated using several factors, such as payment history, total amount of debt, length of credit history and type of credit used.
How credit scores are calculated
Credit scores are calculated based on several variables, such as:
- Payment history: whether you have paid your debts on time or incurred delinquencies;
- Outstanding debt: the amount of money you still owe on your credit cards or loans;
- Length of time you have been using credit: the longer you have had access to credit, the better your score;
- Type of credit used: having a healthy mix of different types of credit (e.g., credit cards and mortgage loans) can be beneficial to your score.
Credit scores are a critical tool for financial institutions in determining whether an applicant is eligible for a loan or credit card.
These scores are based on an individual's credit history, which includes information such as timely payment of obligations, amount of debt and ability to repay.
A good credit score can be the key to obtaining a loan with a favorable interest rate or a credit card with exclusive benefits.
On the other hand, a bad credit history can limit the options available and increase the costs associated with the loan or card.
Improving your credit history
Improving your credit history is an important task if you want to access loans with better conditions and higher amounts in the future.
Here are some tips on how to do it:
- Pay your debts on time: this is the most important factor that determines your credit score. Make sure you pay your bills on time and do not accumulate debts.
- Reduce your outstanding balances: if you have balances on your credit cards, try to reduce them to reduce your level of indebtedness.
- Don't close all your cards: keeping some cards open in the long term can improve your credit history, but make sure you don't have too many open at the same time.
- Keep a good balance: having a balance between your income and expenses can indicate to lenders that you are financially responsible.
- Check your credit report: make sure there are no errors on your report and correct any problems you find.
Check your credit report regularly
One of the most important things you can do to maintain a good credit history is to review your credit report periodically.
This detailed record of your credit history includes information about your loans, credit cards and other types of debt, as well as your payments and balances.
Pay all your bills on time
It is crucial that you pay all of your bills on time, whether they are credit cards, loans, utility bills or anything else you have to pay.
Late payments can have a negative impact on your credit history and lower your score.
If you have trouble paying on time, consider setting reminders or scheduling automatic payments to avoid delays.
Keep your balances low on your existing credit accounts
One of the most effective ways to improve your credit history is to keep your balances low on your existing credit accounts.
This means avoiding excessive charges on your credit cards and making sure you pay your balances in full each month.
If you have many credit accounts, choose a few to keep and close the others.
You may also consider consolidating your debts into one account with a lower interest rate.
Don't apply for too much new credit at one time
Applying for too much new credit at one time can negatively affect your credit score.
Each time you apply for credit, an inquiry is made on your credit history and this is known as a "hard inquiry".
These hard inquiries can lower your credit score by up to 5 points each.
Focus on establishing a solid long-term credit history
One of the best ways to improve your credit history is to establish a good long-term credit history.
This means demonstrating a consistent ability to manage your finances and debt.
As you pay your bills on time and keep your balances low, your credit rating will improve over time.
If you have an account that is in good shape and that you've had for a long period of time, don't close it.
Conclusion
In summary, credit is a financial tool that allows individuals and businesses to borrow money to make large purchases or investments.
Credit scores are a measure of a person's ability to repay debts on time and are used by lenders to determine whether they will grant a loan and at what interest rate.
To improve your credit history, it is important to pay your bills on time, maintain low balances on your credit cards and limit the number of credit inquiries you make.
It is important to take steps to improve your credit score and be responsible with your personal finances.